Often, during the design phase, decision of the warehouse storage medium has to be factored in.
The choices of the type of racking is very much dependent on the inventory profile.
Factors such as dimensions of inventory, type and size of pallets, number of SKU, quantity per SKU, fast moving items versus slow moving items and inventory turns have to be considered for a suitable racking configuration.
In addition, you have to take into account the physical warehouse layout shapes, spacing between pillars and clear ceiling height too.
Some of the commonly seen storage mediums in a typical warehouse are shared below.
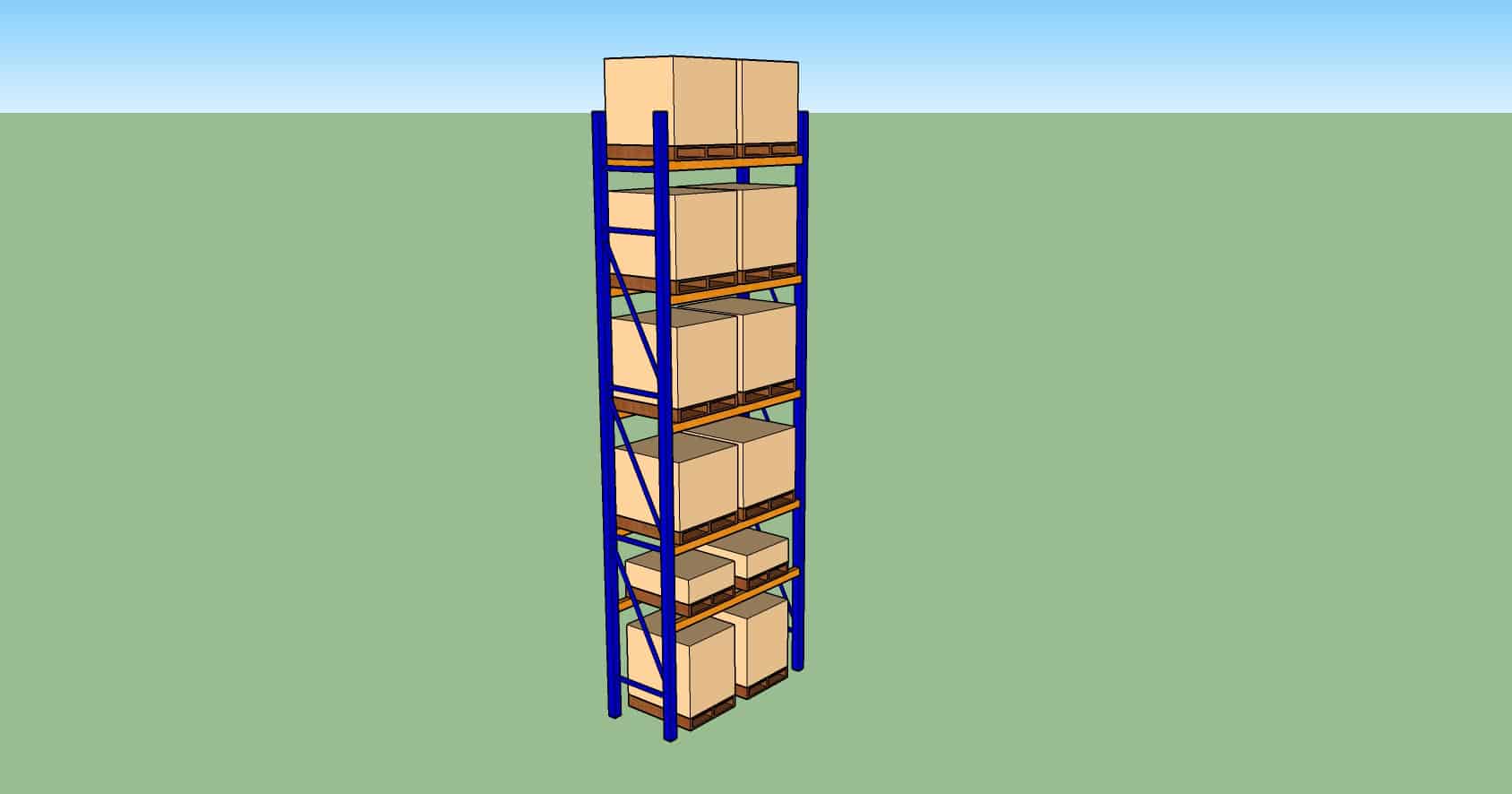
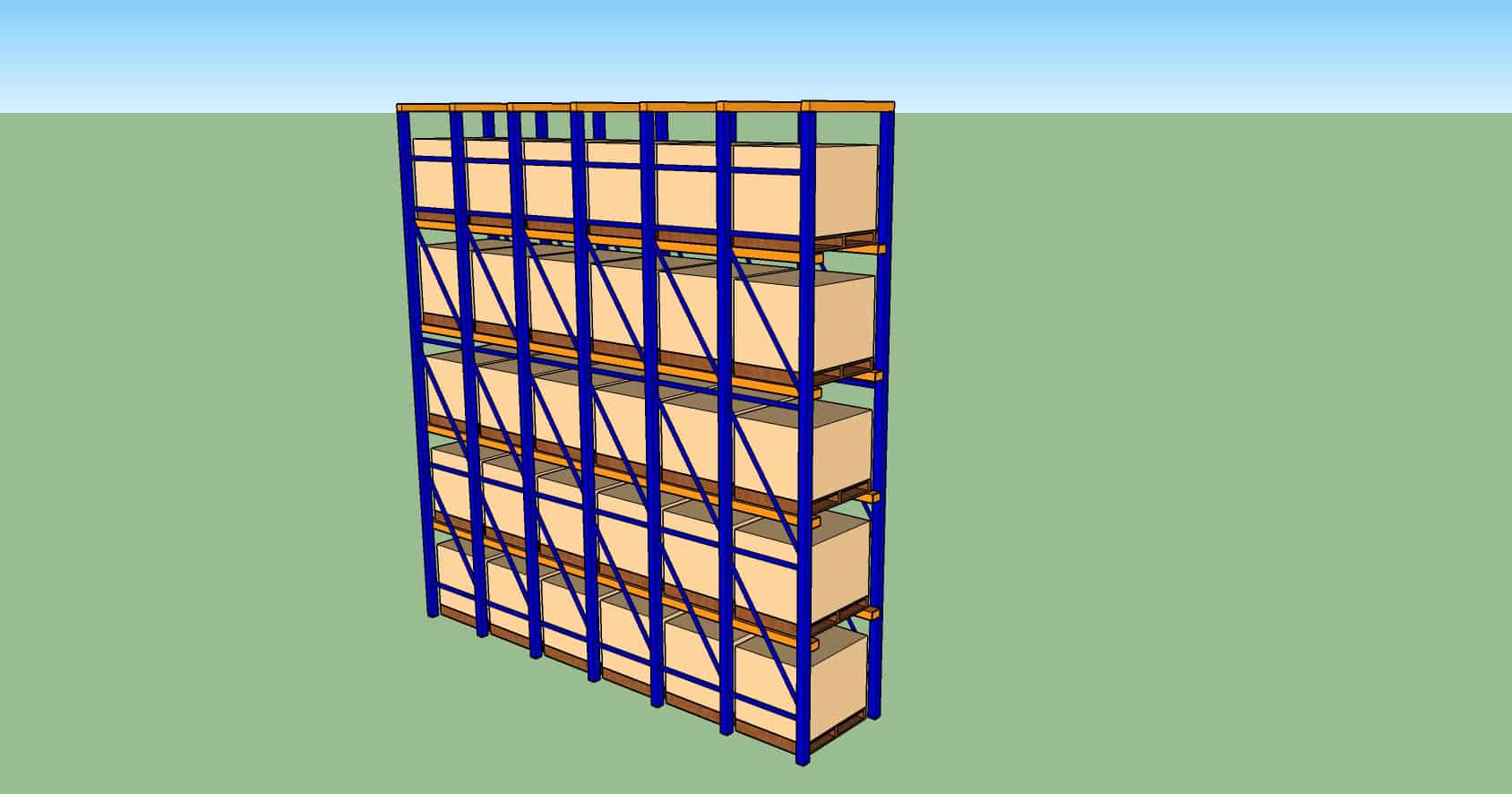
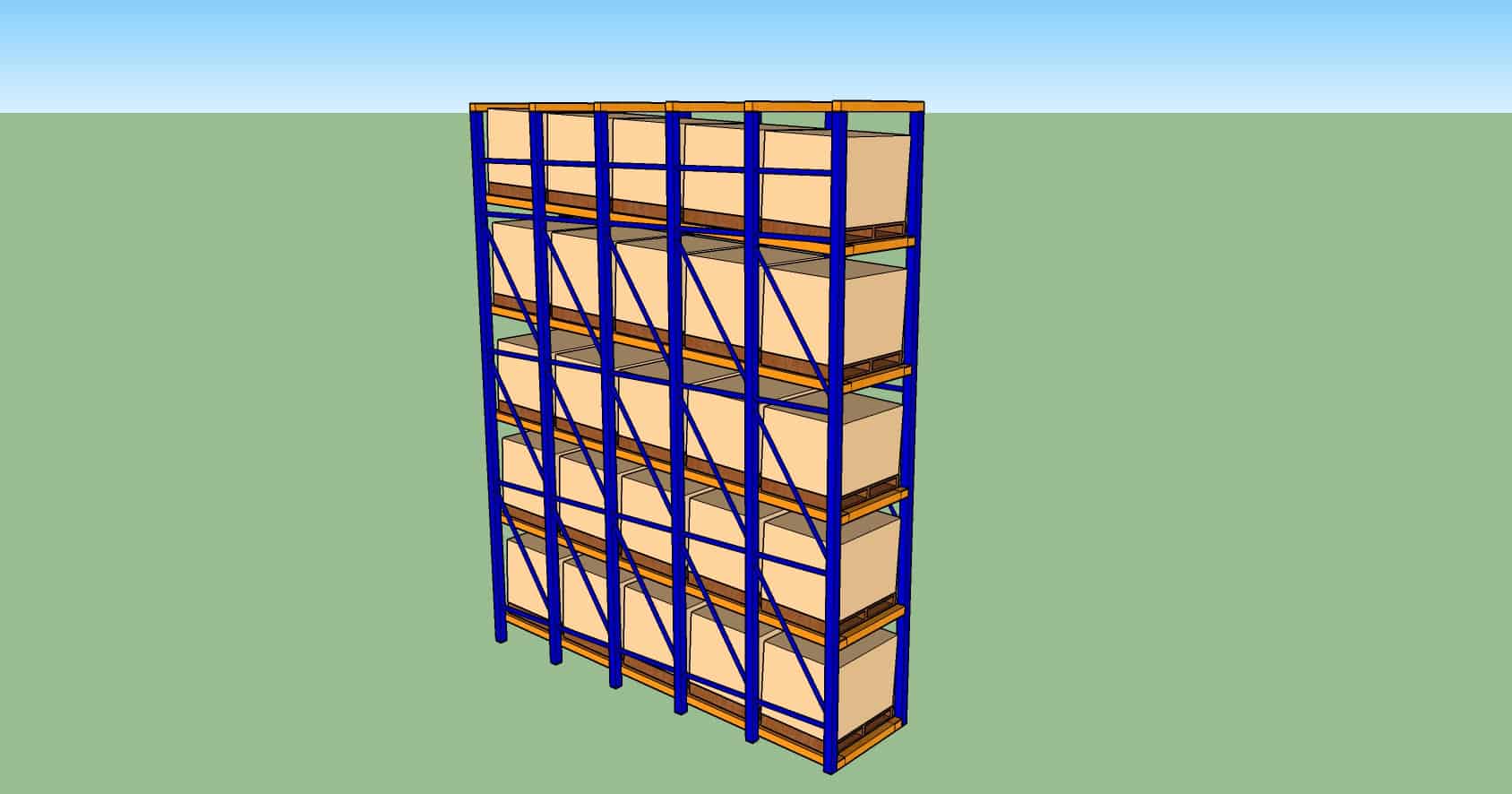
Selective Racking
Characteristics
- Most commonly seen in warehouses. Suitable for wide range of products.
Pro
- Easily fabricated
- Horizontal beams can be adjusted easily if no in-rack sprinklers in place.
- Different levels can have different heights.
- Accessible to every pallet.
- Conventional MHE is suitable.
Con
- Floor space not fully optimized. Aisles are required for MHE movement.
Drive-In Racking
Characteristics
- Suitable for warehouse with small variation of SKU and high number of pallets.
- Last in first out.
Pro
- Higher storage density compared to selective racking.
- Conventional MHE is suitable.
Con
- If batch number is a factor to be considered, may not be suitable.
- To get the pallets stored in the back of upper level, you need to remove the pallets at the bottom level (to give way to the MHE).
- Not accessible to every pallet.
Push Back Racking
Characteristics
- Similar to Drive-In Racking. Suitable for warehouse with small variation of SKU and high number of pallets.
- Last in first out.
- Unlike Drive-In Racking, to get the pallets stored in the back of upper level, you just have to remove the front pallets of that particular level.
Pro
- Higher storage density compared to selective racking.
- Conventional MHE is suitable.
Con
- If batch number is a factor to be considered, may not be suitable.
- Not accessible to every pallet.
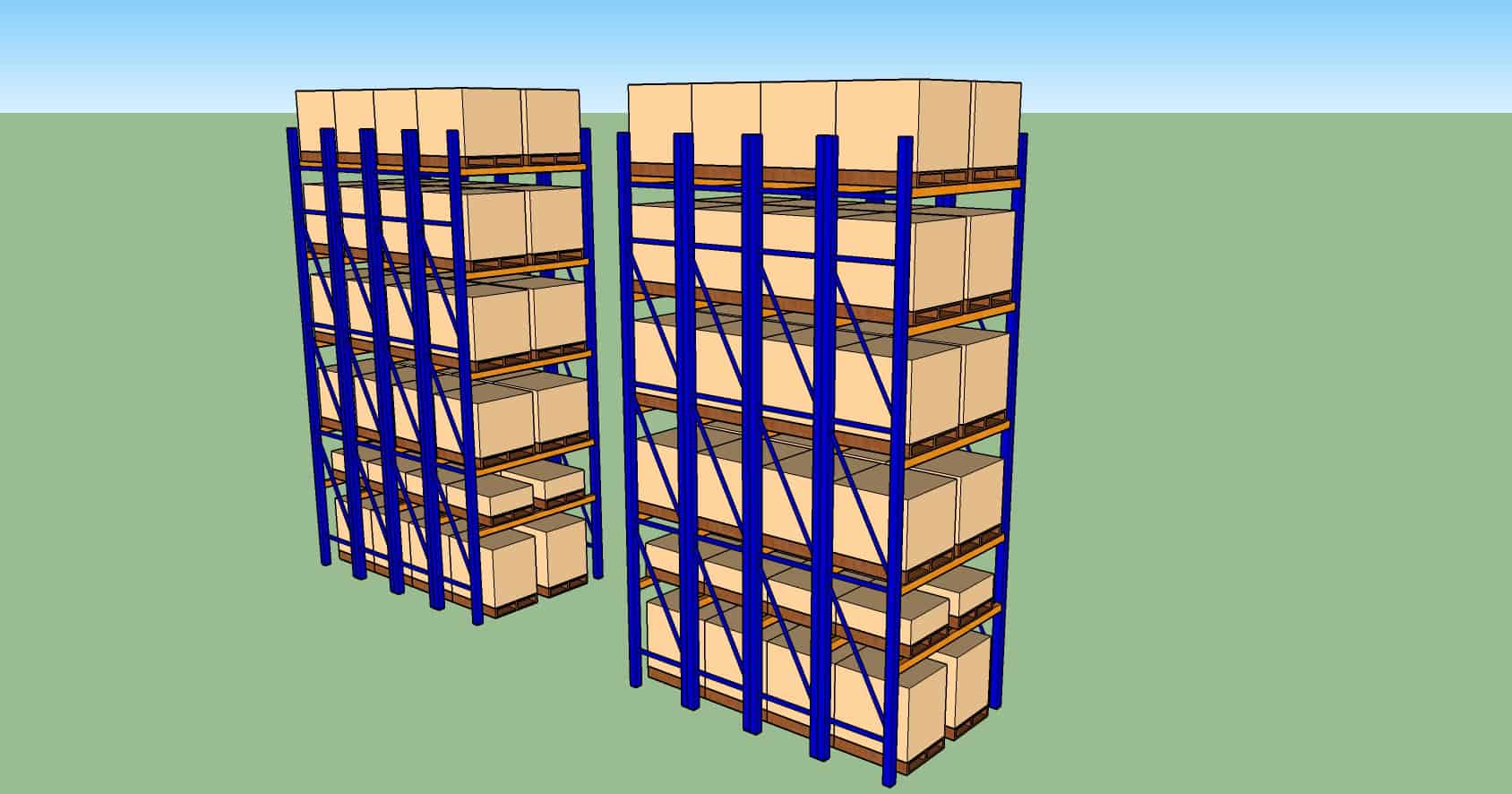
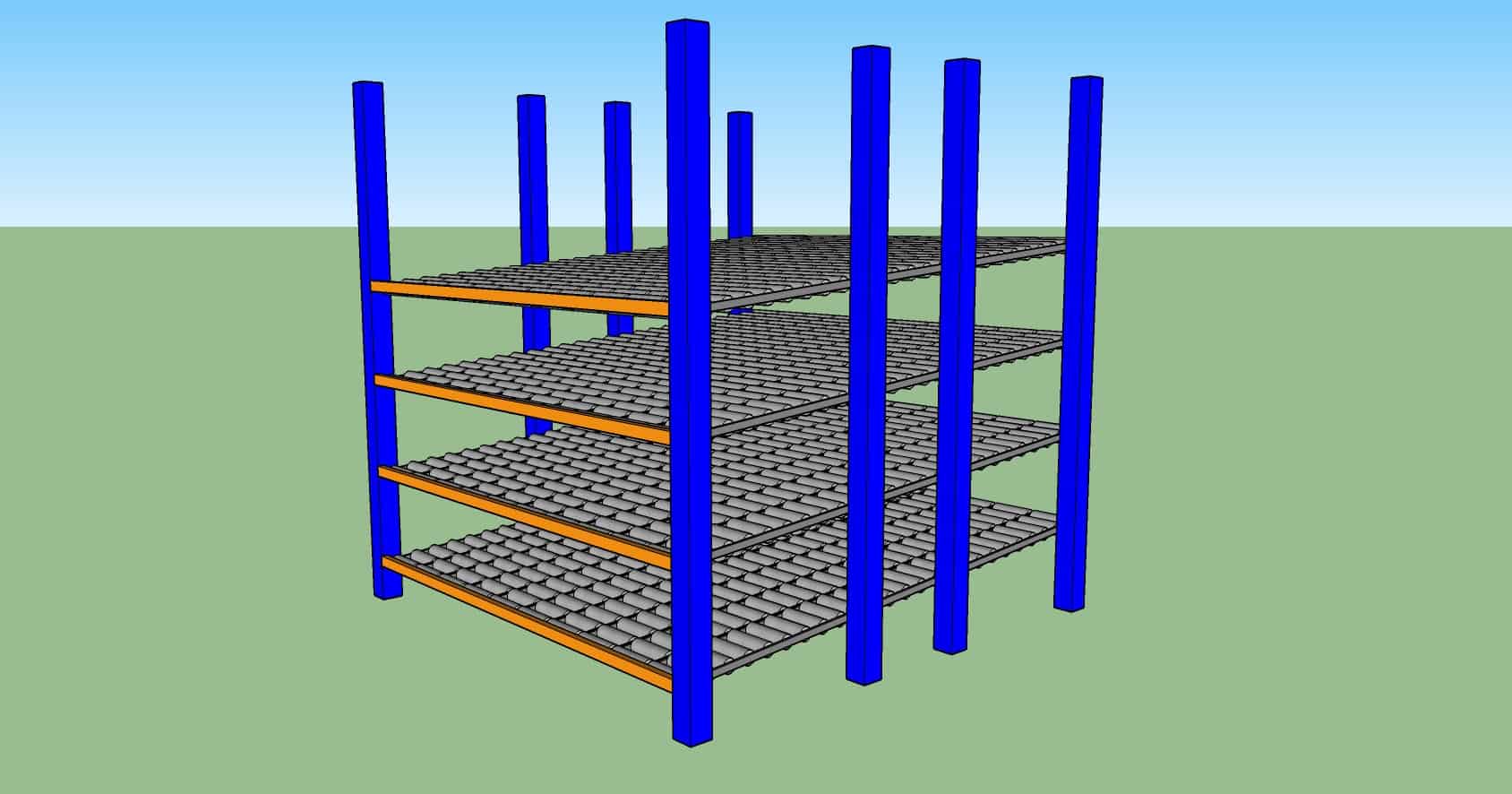
Double Deep Racking
Characteristics
- A variation of Selective Racking, where another layer of pallets are stored behind the front row. MHE in the aisle is able to fork both the front and back pallets with special forks.
- Suitable for products with low SKU variation and high volume.
Pro
- Higher storage density compared to selective racking.
Con
- Not accessible to every pallet.
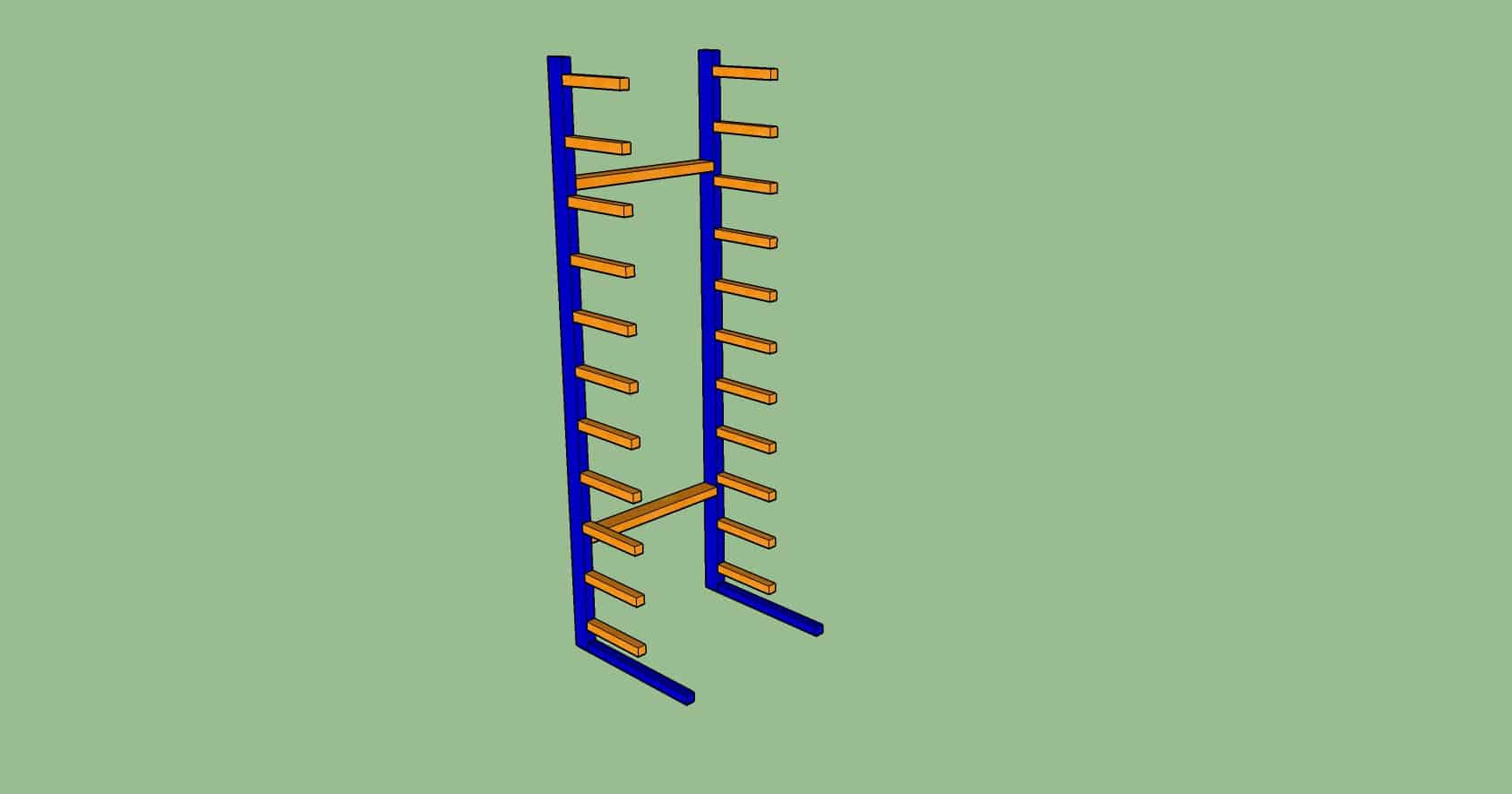
Cantilever Rack
Characteristics
- Suitable for products of odd and long dimensions (such as pipes and tubes).
- Sheets can be added to form a base for the arms if required.
Pro
- Flexibility in terms of storing odd shaped inventory.
Con
Support for the inventory are at the arms.
Even if you setup the base and insert partition, the total weight of that level still has to be within the arms’ limit.
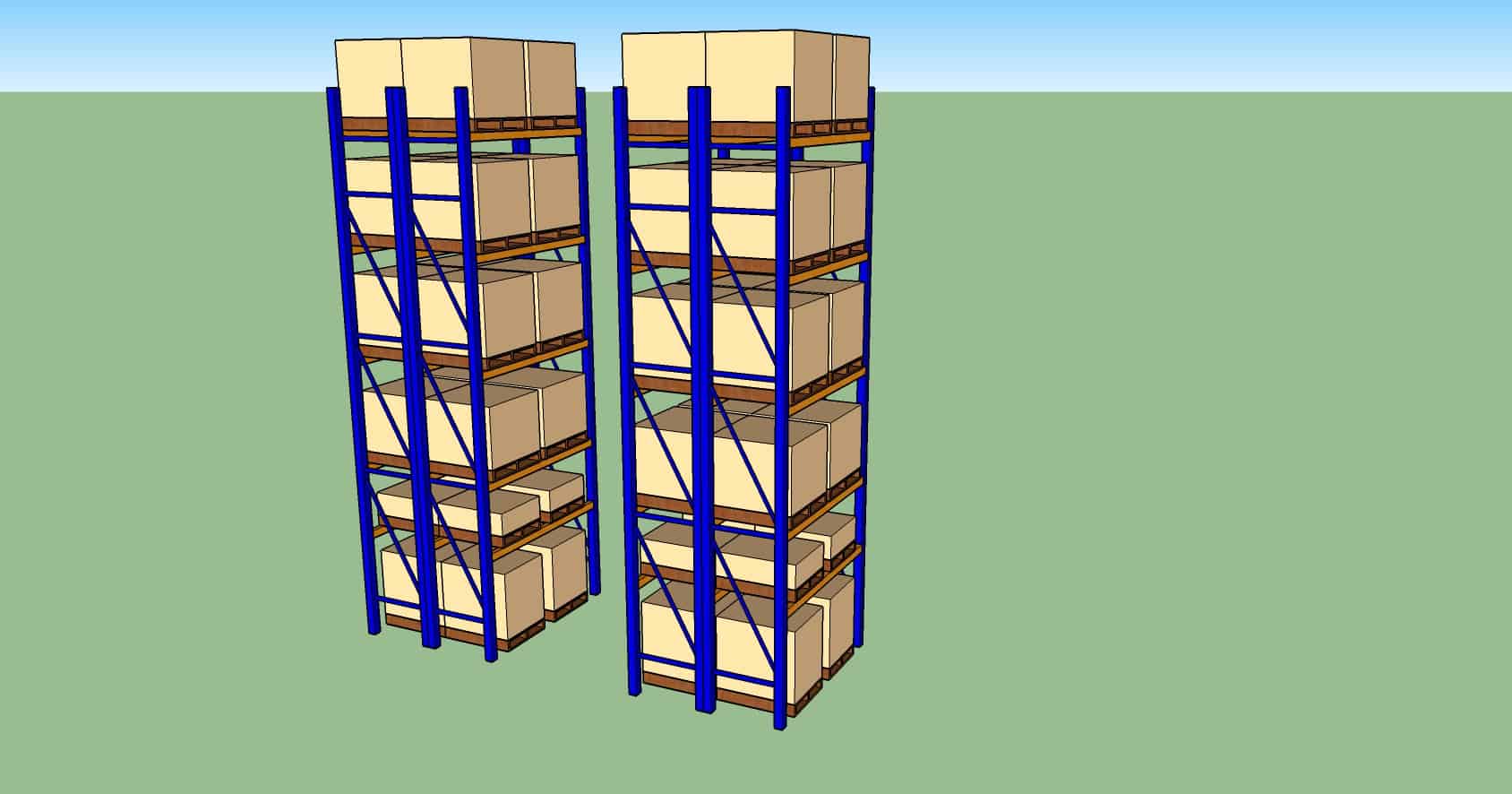
VNA (Very Narrow Aisle)
Characteristics
- Commonly seen in warehouses, after selective racking.
- Aisles are narrow and MHE normally is dedicated to particular aisle.
- Suitable for warehouses with limited storage capacity.
Pro
- Better utilization of floor area compared to selective racking.
- Dedicated MHE per lane, reduction of travelling distance.
Con
- Large number of MHE and pickers required.
- Pick face may be affected (if pickers cannot manually pick from the ground level).
Flow Rack
Characteristics
- Normally for picking of loose items and not pallets.
- Suitable for fast moving items.
- Works well together with conveyor system.
Pro
- Higher density of storage space.
- Multiple pick faces.
- Picker taking care of designated area. Less walking distances compared to selective racking.
Con
- Storage of product is not as much as selective racking. More frequent replenishment required.
- Air space unutilized. Based on human height.
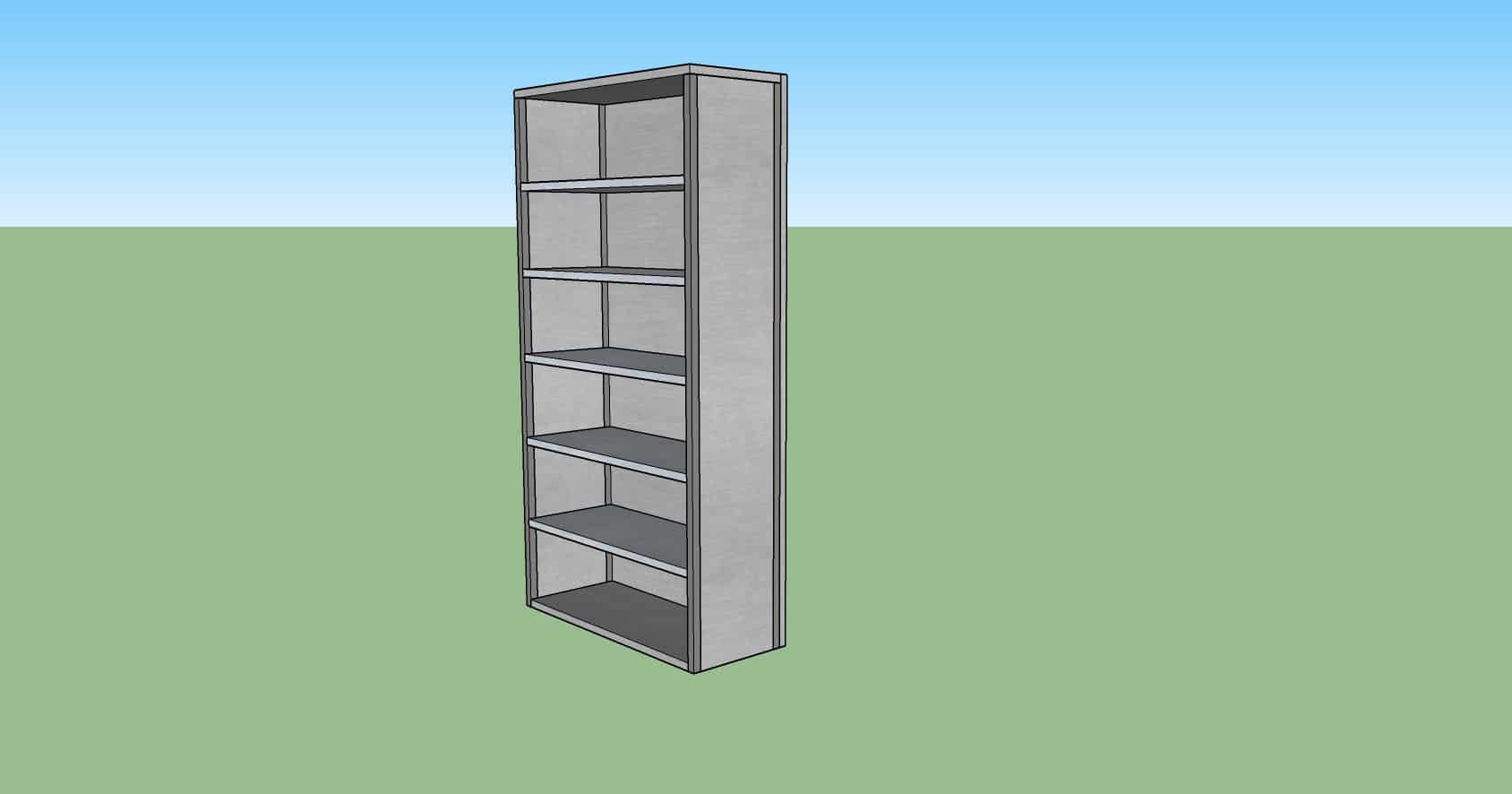
Shelving
Characteristics
- Storage of items of small sizes and small quantity.
Pro
- Flexible in shelving heights.
Con
- Low support weight.
- Small dimensional inventory.